iCRM Report
Order Here
iCRM helps you and your loved ones lower cancer risk to stop cancer before it starts.
**Please make sure you are registered and logged in first to use this service.
4 Steps to Get the iCRM Report
1. Get lab results

2. Upload the results
3. Select cancer types to report

4. Make the payment

Step 1: Get your information ready for iCRM
- Personal Information (age, smoking & drinking habits, physical activities, etc.)
- Lab Test Results**
- Comprehensive Wellness Profile
- Complete Blood Count
- WBC—White blood cells are the body’s primary defense against disease.
- RBC—Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen to and carbon dioxide away from all cells.
- Hemoglobin—A chemical compound inside red cells that transports oxygen through the blood stream to all cells of the body.
- Hematocrit—Hematocrit measures the amount of space red blood cells take up in the blood.
- MCV—MCV reflects the size of red blood cells by expressing the volume occupied by a single red blood cell.
- MCH Mean—Corpuscular Hemoglobin is one way to measure the average hemoglobin concentration within red blood cells.
- MCHC—MCHC measures the average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells.
- RDW—Red cell distribution width (RDW) is a calculation of the variation in the size of your RBC’s.
- Platelets—Blood cell particles involved with the forming of blood clots.
- Neutrophils, Lymphocytes, Monocytes, Eosinophils, and Basophils deal with white blood cell function. Important to the body’s defense against infection and also important in the assessment of nutritional status. These tests are based upon percentages.
- Neutrophils (Absolute), Lymphocytes (Absolute), Monocytes (Absolute), Eosinophils (Absolute), and Basophils (Absolute) deal with white blood cell function.
- Liver Profile
- Protein, Total—Proteins are the most abundant compound in serum.
- Albumin, Serum—Albumin is the major constituent of serum protein (usually over 50%).
- Globulin, Total—Globulin, a larger protein than albumin, has many diverse functions such as, the carrier of some hormones, lipids, metals, and antibodies.
- Albumin/Globulin Ratio—Calculated by dividing the albumin by the globulin.
- Bilirubin, Total—A byproduct of the breakdown of hemoglobin from red blood cells in the liver, bilirubin is a good indication of the liver’s function.
- Alkaline Phosphatase—A body protein important in diagnosing proper bone and liver functions.
- Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)—An enzyme found mostly in the heart, muscles, liver, kidney, brain, and red blood cells.
- Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST or SGOT)—An enzyme found in skeletal and heart muscle, liver and other organs.
- Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT or SGPT)—An enzyme found primarily in the liver.
- GGT—Also known as Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, GGT helps detect liver and bile duct injury.
- Kidney Panel
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)—A by-product of protein metabolism eliminated through the kidneys.
- Creatinine, Serum—Creatinine is the waste product of muscle metabolism. Its level is a reflection of the body’s muscle mass.
- Uric Acid—Another by-product of protein metabolism eliminated through the kidneys.
- BUN/Creatinine—Ratio calculated by dividing the BUN by the Creatinine.
- Glomerular Filtration (eGFR)—Provides an assessment of the filtering capacity of the kidney.
- Glucose
- Glucose— Glucose, formed by the liver, is the primary source of energy for most cells.
- Lipid Profile
- Cholesterol, Total—Cholesterol is a critical fat that is a structural component of cell membrane and plasma lipoproteins, and is important in the synthesis of steroid hormones, glucocorticoids, and bile acids.
- HDL Cholesterol—High-density lipoproteins are believed to take cholesterol away from cells and transport it back to the liver for processing or removal. They have become known as the “good” cholesterol.
- LDL Cholesterol—Low-density lipoproteins contain the greatest percentage of cholesterol and may be responsible for depositing cholesterol on the artery walls. For that reason, they are known as the “bad” cholesterol.
- Cholesterol/HDL Ratio—This ratio is calculated by dividing the total cholesterol by the HDL cholesterol and is used for determining relative risk for developing cardiovascular heart disease.
- Triglycerides—Triglycerides are fat in the blood responsible for providing energy to the cells of the body.
- Learn more about the Comprehensive Wellness Profile at DirectLabs.com
- Complete Blood Count
- Urinalysis: only needed for cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, and prostate cancer risk predictions
- A regular urinalysis often includes the following tests:
- Urine’s appearance
- Urine color
- Acidity (pH)- The pH level indicates the amount of acid in urine. Abnormal pH levels may indicate a kidney or urinary tract disorder.
- A measure of concentration, or specific gravity, shows how concentrated particles are in your urine.
- Protein– low levels of protein in urine are normal.
- Sugar– normally the amount of sugar (glucose) in urine is too low to be detected.
- Ketones– as with sugar, any amount of ketones detected in your urine could be a sign of diabetes and requires follow-up testing.
- Bilirubin– a product of red blood cell breakdown.
- Evidence of infection. If either nitrites or leukocyte esterase — a product of white blood cells — is detected in your urine, it may be a sign of a urinary tract infection.
- Blood. Blood in your urine requires additional testing — it may be a sign of kidney damage, infection, kidney or bladder stones, kidney or bladder cancer, or blood disorders.
- White blood cells (leukocytes) may be a sign of an infection.
- Red blood cells (erythrocytes) may be a sign of kidney disease, a blood disorder or another underlying medical condition, such as bladder cancer.
- Bacteria or yeasts may indicate an infection.
- Casts — tube-shaped proteins — may form as a result of kidney disorders.
- Crystals that form from chemicals in urine may be a sign of kidney stones.
- Learn more about a urinalysis test at MayoClinic.com
- A regular urinalysis often includes the following tests:
- Comprehensive Wellness Profile
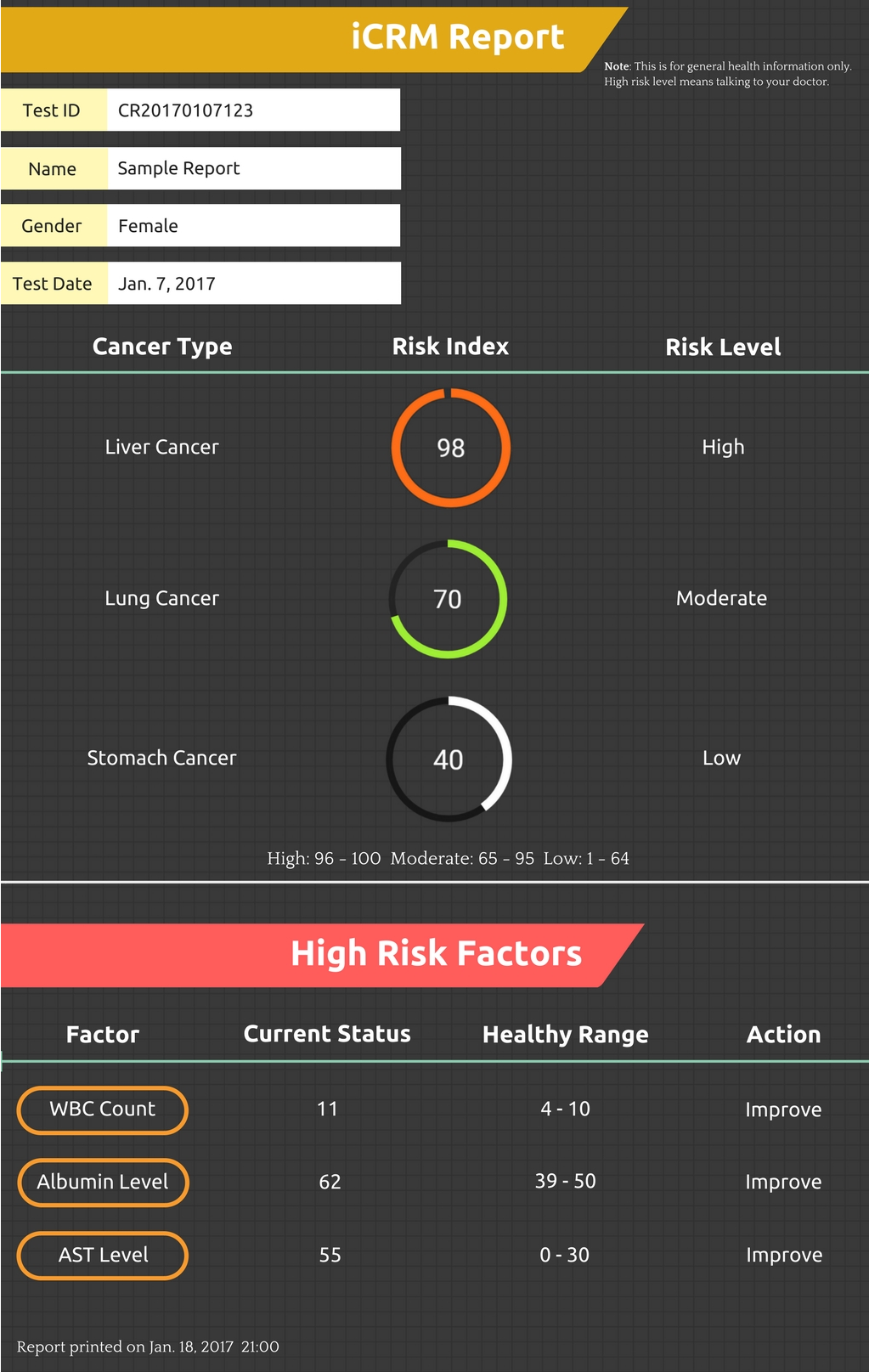
** Your most recent lab test results will tell your current cancer risk level and your previous lab test results would help establishing a benchmark.
** The lab tests are typically covered by health insurance.
** Lab tests can also be ordered online fromlocal labs.
Step 2: Upload your information
You can upload your lab test results information in the iCRM Report page (once you click Order Here on this page).
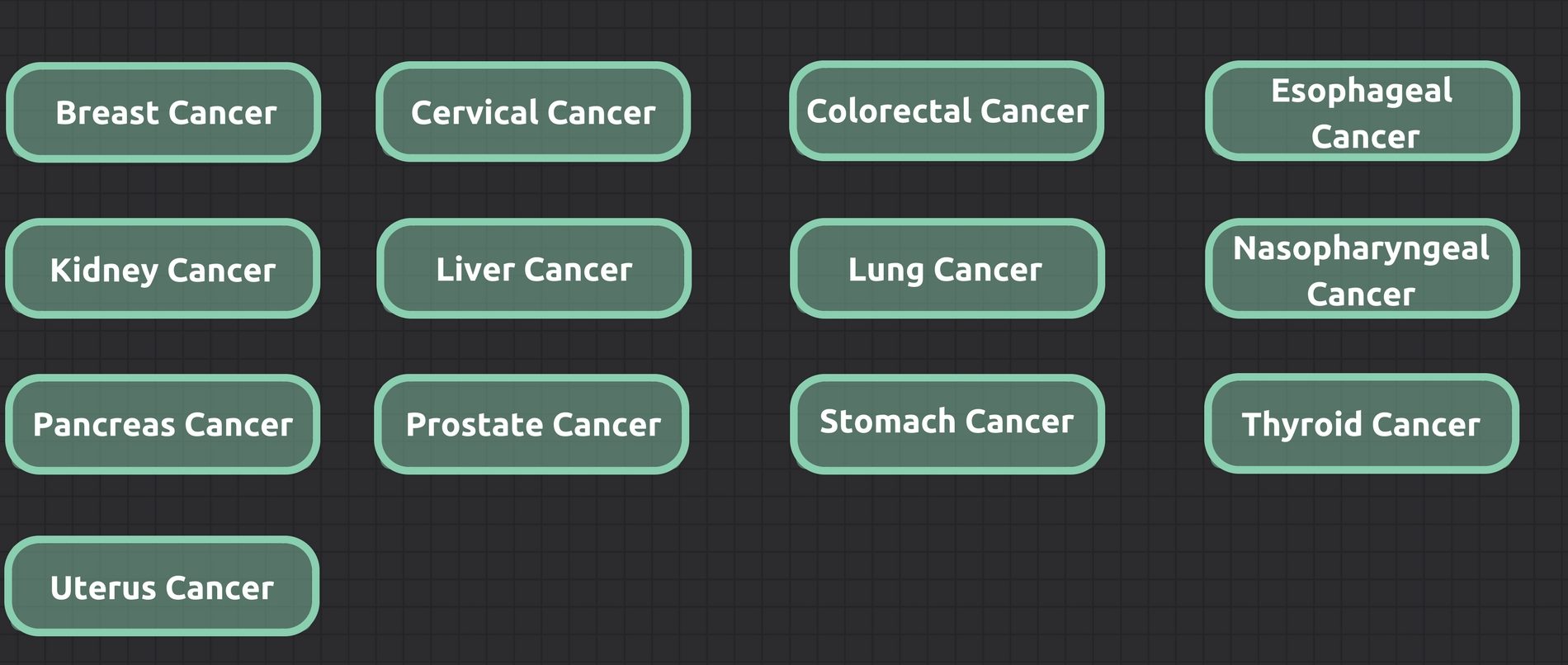
Step 3: Select the types of cancer risk to predict and evaluate
iCRM currently offers 13 types of cancer prediction and evaluation services.
Step 4: Make the payment
An iCRM report costs $49.99. The report will be sent to you within 24 to 72 hours after payment.
Order Here
iCRM Report Sample